Supporting Multiple Certificates with Existing Public IP Addresses
Question
A global sports news company has hosted its website on Amazon EC2 instance using a single Public IP address & is front-ended by TLS-enabled Application Load Balancer.
For an upcoming mega sports event, they plan to launch a new website on the existing Amazon EC2 instance.
The company has registered a different domain name & possesses a separate TLS certificate for this new website. As an AWS consultant to this company, which of the following recommendations will you provide to support multiple certificates with existing Public IP addresses in the most cost-effective way?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer: D.
ALB supports Server Name Indication (SNI), enabling hosting multiple domain names with different TLS certificates behind a single ALB.
With SNI, multiple certificates can be associated with listeners in ALB, enabling each web application to use separate certificates.
The below diagrams shows the process which takes place when a client tries to access a website.
Client Browser starts a TLS handshake by sending a ClientHello message which consists of protocol version, extensions, cipher suites, and compression techniques.
Based on browser capabilities, ALB responds with a valid certificate for a domain name of the requested web application.
Option A is incorrect as launching additional ALB will work.
But it will incur additional cost & admin work for setup.
Option B is incorrect as using wildcard certificates can be used for related sub-domains & not different domains.
Option C is incorrect as using SAN certificates, for any new addition of domain, all certificates need to revalidate with certificate authority.
For more information on Amazon ALB SNI support, refer to the following URL-
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-application-load-balancer-sni/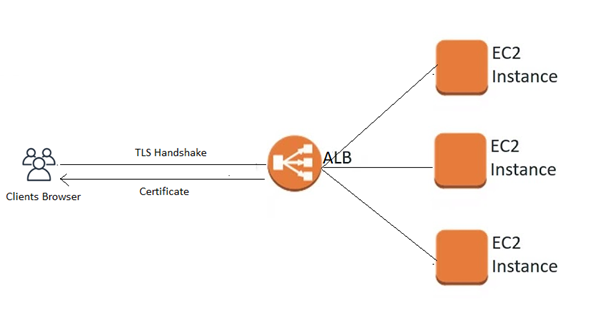
The scenario involves a global sports news company that has hosted its website on an Amazon EC2 instance using a single Public IP address and is front-ended by a TLS-enabled Application Load Balancer. The company plans to launch a new website on the existing Amazon EC2 instance with a different domain name and a separate TLS certificate.
To support multiple certificates with existing Public IP addresses in the most cost-effective way, the recommended approach is to use multiple TLS certificates on ALB using Server Name Indication (SNI). This approach is recommended because it allows for the use of multiple certificates on a single load balancer, which is cost-effective as it eliminates the need to launch an additional load balancer or use wildcard certificates.
SNI is an extension of the TLS protocol that enables a server to present multiple certificates on the same IP address and port number. When a client initiates an SSL/TLS handshake with the server, the client sends the requested hostname as part of the handshake. The server uses this hostname to select the appropriate certificate to present to the client.
Therefore, by using SNI, the ALB can be configured to use multiple certificates, and the appropriate certificate will be presented to the client based on the requested hostname. In this case, the ALB can be configured to use the existing certificate for the original domain and the new certificate for the new domain.
Option A, Launch an additional TLS-enabled ALB front-ending Amazon EC2 instance with different certificates for each domain, is not cost-effective as it requires the launch of an additional load balancer.
Option B, Use Wildcard certificates on ALB matching old and new domain names, is not recommended as it can be costly and less secure since wildcard certificates can be used to secure any subdomain, potentially exposing the website to security risks.
Option C, Use a single certificate on ALB and add Subject Alternative Name (SAN) for an additional domain name, is not recommended as it requires purchasing a new certificate that supports SANs, which can be costly, and can also lead to operational overhead in managing the certificate. Additionally, some clients may not support SANs, leading to compatibility issues.