AWS STS API Integration Guide
Question
Your organization has an AWS setup and planning to build Single Sign On for users to authenticate with on-premise Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) and let users login to AWS console using AWS STS Enterprise Identity Federation.
Which of the following API should be used with AWS STS service after you authenticate with your on-premise?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: A.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/STS/latest/APIReference/API_AssumeRoleWithSAML.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_providers_saml.html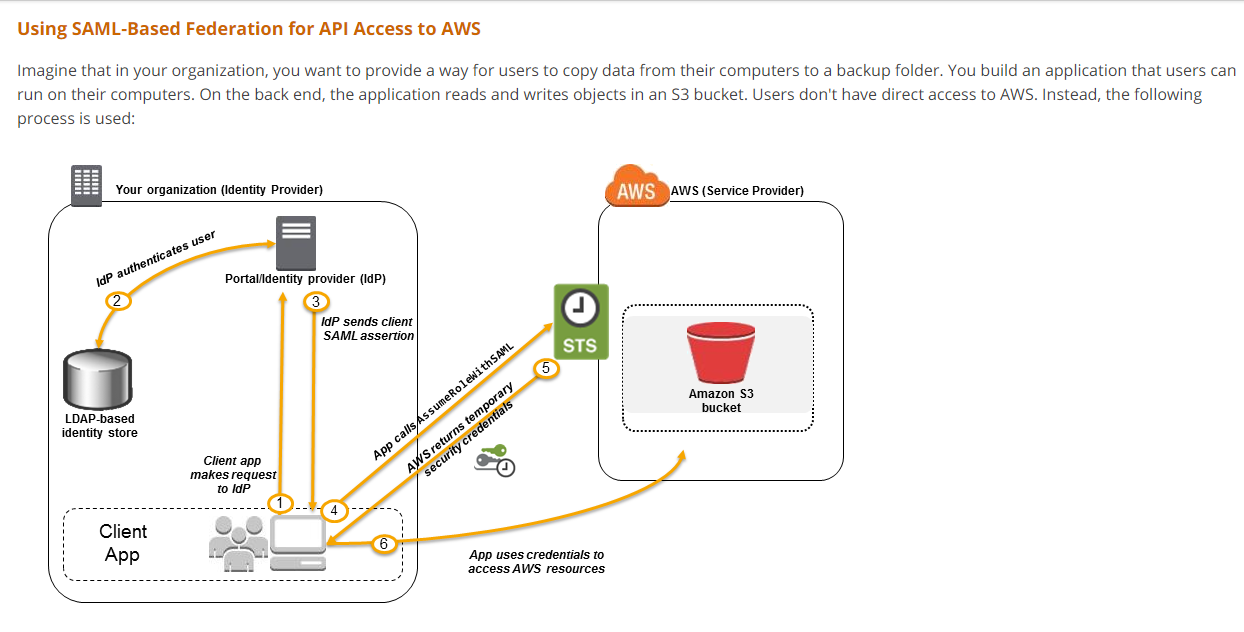
The correct API that should be used with AWS STS service after authenticating with your on-premise Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is AssumeRoleWithSAML. Therefore, the answer is A.
Here's a detailed explanation:
AWS Security Token Service (STS) is a web service that enables you to request temporary, limited-privilege credentials for AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) users or for users that you authenticate (federated users).
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials. AWS supports SSO through the use of Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), which is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties.
To use SAML-based SSO with AWS, you need to configure an identity provider (IDP) that supports SAML 2.0, such as Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), and map SAML attributes to IAM roles in AWS.
Once the SSO setup is complete, users can access AWS services and resources using the AWS Management Console or AWS command line interface (CLI) using temporary security credentials obtained via the AssumeRoleWithSAML API. This API call requests AWS to assume an IAM role based on the SAML assertion provided by the IDP.
The AssumeRoleWithSAML API call takes the following parameters:
RoleArn: The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the IAM role to assumePrincipalArn: The ARN of the SAML provider in IAM that describes the IdPSAMLAssertion: The base-64 encoded SAML assertion provided by the IdP
The GetCallerIdentity API call returns the AWS account ID and IAM user or role that made the request, and is not used for SSO.
The AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity API call is used when you want to grant access to AWS resources to users who are authenticated outside of AWS with a web identity provider, such as Amazon, Facebook, or Google.
The GetFederationToken API call is used to obtain temporary security credentials for IAM users who require temporary access to resources. It is not used for SSO.
Therefore, the correct answer is A. AssumeRoleWithSAML should be used with AWS STS service after authenticating with your on-premise Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) to enable SSO with AWS.