Question 220 of 490 from exam 400-051: CCIE Collaboration
Question
Refer to the exhibit.
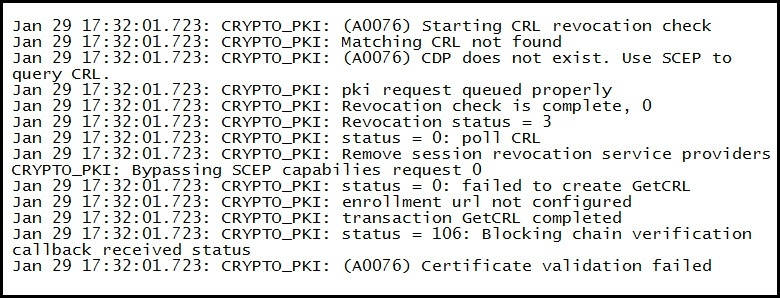
The public key infrastructure debugs are generated on a Cisco IOS VPN router for a failed certification validation on an incoming connection from an IP phone client.
Which option is a possible solution for this problem?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E.C.
When a certificate is issued, it is valid for a fixed period of time.
Sometimes a CA revokes a certificate before this time period expires; for example, due to security concerns or a change of name or association.
CAs periodically issues a signed list of revoked certificates.
Enabling revocation checking forces the IOS router to check that the CA has not revoked a certificate every time it uses that certificate for authentication.
When you enable revocation checking during the PKI certificate validation process, the router checks certificate revocation status.
It can use either CRL checking or Online Certificate Status Protocol or both, with the second method you set in effect only when the first method returns an error, for example, that the server is unavailable.
With CRL checking, the router retrieves, parses, and caches Certificate Revocation Lists, which provide a complete list of revoked certificates.
OCSP offers a more scalable method of checking revocation status in that it localizes certificate status on a Validation Authority, which it queries for the status of a specific certificate.