The Roles of Devices in a WAN
Question
Which of the following describes the roles of devices in a WAN? (Choose three.)
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E. F.ADE
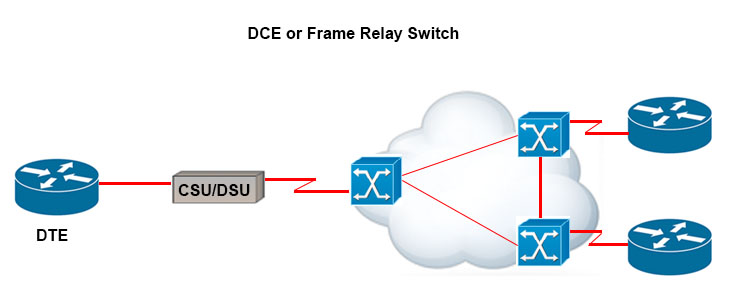
The idea behind a WAN is to be able to connect two DTE networks together through a DCE network. The network's DCE device (includes CSU/DSU) provides clocking to the DTE-connected interface (the router's serial interface).
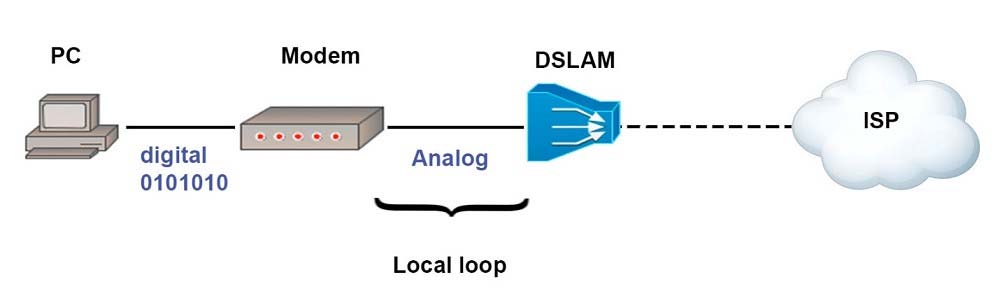
A modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair telephone line and demodulates the incoming analog signal and converts it to a digital signal for the digital device. A CSU/DSU is used between two digital lines -
For more explanation of answer D, in telephony the local loop (also referred to as a subscriber line) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider's network. Therefore, a modem terminates an analog local loop is correct.
Wide Area Networks (WANs) are used to connect geographically dispersed networks or devices. Various devices are involved in the functioning of a WAN. Let's discuss the roles of these devices in detail:
A. A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) terminates a digital local loop: A digital local loop refers to the transmission of digital data over a local loop or local access network (LAN). A CSU/DSU is a device that connects a digital circuit to a network. It acts as a mediator between the digital circuit and the WAN. The CSU/DSU converts digital data into a form that can be transmitted over WAN links. It also provides the clocking necessary for the WAN interface.
B. A modem terminates a digital local loop: A modem (short for modulator-demodulator) is a device that converts digital signals into analog signals (modulation) and vice versa (demodulation). A modem terminates the digital local loop by converting digital signals from the computer into analog signals that can be transmitted over a telephone line. At the receiving end, the modem converts the analog signals back into digital signals that can be understood by the computer.
C. A CSU/DSU terminates an analog local loop: An analog local loop refers to the transmission of analog data over a local loop or LAN. A CSU/DSU terminates an analog local loop in the same way as it terminates a digital local loop. It mediates between the analog circuit and the WAN and provides clocking for the WAN interface.
D. A modem terminates an analog local loop: A modem can also terminate an analog local loop. It converts analog signals from the computer into analog signals that can be transmitted over a telephone line. At the receiving end, the modem converts the analog signals back into digital signals that can be understood by the computer.
E. A router is commonly considered a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) device: A DTE is a device that originates or terminates digital data. A router is a DTE device because it originates and terminates digital data. A router receives digital data from a LAN and transmits it over a WAN link. Similarly, it receives digital data from a WAN link and transmits it over a LAN.
F. A router is commonly considered a DCE (Data Communications Equipment) device: A DCE is a device that provides clocking for a WAN link. A router is a DCE device because it provides clocking for a WAN link. The clocking ensures that the data is transmitted at the correct rate over the WAN link.
Therefore, the correct answers are A, E, and F. A CSU/DSU terminates a digital local loop and an analog local loop, a router is commonly considered a DTE device and a DCE device.
